Biodegradable plastics break down under natural conditions like soil or sand, or specific conditions such as composting, anaerobic digestion, or aqueous environments. This degradation is driven by microorganisms, resulting in carbon dioxide (CO2) and/or methane (CH4), water (H2O), mineral salts, and new biomass.
Based on raw material sources, biodegradable plastics are classified into bio-based (e.g., PLA, PHA) and petrochemical-based (e.g., PBAT, PBS, PPC, PGA) .
-For film bag-
PBAT+PLA+starch, PBAT+calcium carbonate
-For tableware-
PLA+PBAT+talc powder, PLA+plant fiber+silica fume, PBS+PLA+calcium carbonate, PBS+bamboo powder+starch, PBS+PLA+straw, straw powder+PLA+talc powder, PLA+PBAT+PHA+talc powder, and etc.
-Feeding system-
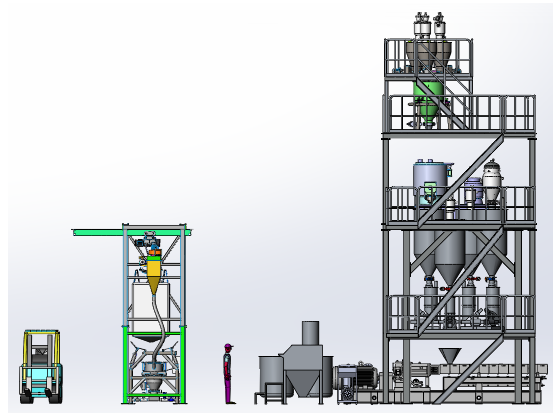
1. Starch, liquid, and additives are transported to the batching system through vacuum loading, and then pre treated by a mixer before being transported to the saving silo.
2. The remaining raw materials are transported to various saving silos through vacuum loading.
3. Based on the settings, the above materials enters the loss-in-weight feeder from the solid. It then goes into the extruder after being measured.
-Twin screw extruder-
Raw materials are plasticized, mixed, vacuum-degassed, and pressurized through a twin-screw extruder to produce dozens of finished strands.
-Pelletizing and packaging-
Strands are cooled by stainless steel air-cooled conveyor belt and then cut into pellets by the pelletizer. The screened pellets enter the finished product silo for drying and homogenization, then vacuum sealed and packaged.
| Model | Motor Power(kW) | Screw Speed(rpm) | Througuhput(kg/h) |
| HK73 | 160 | 40-400 | ~300 |
| HK73 MT | 200 | 40-400 | ~400 |
| SK73 | 250 | 40-400 | ~450 |